Types of Lithium Batteries: A Comprehensive Guide
Lithium batteries have revolutionized energy storage due to their high energy density, long life cycles, and efficiency. They are commonly used in applications ranging from consumer electronics to electric vehicles and renewable energy systems. Here, we explore the various types of lithium batteries and their unique characteristics.
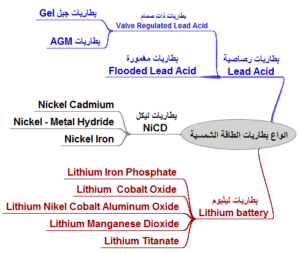
1. Lithium-Ion (Li-ion)
Overview: Li-ion batteries are the most widely used type of lithium batteries, known for their high energy density and versatility. They are commonly found in smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles.
Key Features:
High energy density
Low self-discharge rate
Long cycle life
Applications:
Consumer electronics
Electric vehicles (EVs)
Power tools
Renewable energy storage
Chemistries:
Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LCO): High energy density, used in mobile devices.
Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC): Balanced performance, common in EVs.
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP): High safety and long life, used in renewable storage and EVs.
2. Lithium Polymer (LiPo)
Overview: LiPo batteries use a polymer electrolyte instead of a liquid one, making them lightweight and adaptable to various shapes.
Key Features:
Lightweight and compact
Flexible form factor
Moderate energy density
Applications:
Drones
RC models
Wearable devices
Limitations:
Higher cost compared to other types
Lower energy density than some Li-ion chemistries
3. Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4 or LFP)
Overview: LFP batteries are renowned for their safety, stability, and long cycle life. They are increasingly used in large-scale applications.
Key Features:
Excellent thermal stability
High safety standards
Long cycle life (>2000 cycles)
Applications:
Solar energy storage
Electric buses and trucks
Marine applications
Advantages:
Tolerant to high temperatures
Minimal risk of thermal runaway
4. Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide (NCA)
Overview: NCA batteries offer high energy density and are commonly used in electric vehicles and industrial applications.
Key Features:
High energy density
Long cycle life
Suitable for high-performance applications
Applications:
Electric vehicles
Industrial energy storage
Challenges:
Expensive materials
Limited thermal stability
5. Lithium Titanate (LTO)
Overview: LTO batteries replace the graphite anode in traditional Li-ion batteries with lithium titanate, offering unique advantages.
Key Features:
Rapid charging capability
Extremely long cycle life (>5000 cycles)
High safety profile
Applications:
Electric buses
Grid storage
Military applications
Drawbacks:
Lower energy density
Higher cost
6. Lithium Manganese Oxide (LMO)
Overview: LMO batteries are known for their high power output and safety features, making them suitable for high-drain devices.
Key Features:
High thermal stability
Good safety performance
Moderate energy density
Applications:
Power tools
Electric bikes
Medical devices
Challenges:
Shorter cycle life compared to other chemistries
Conclusion
Lithium batteries come in various types, each tailored for specific applications and performance requirements. While Li-ion batteries dominate the consumer electronics and EV markets, specialized chemistries like LFP and LTO are gaining traction in renewable energy and industrial applications. Understanding these differences helps in selecting the right battery type for your needs, whether it’s for a smartphone, solar energy system, or electric vehicle.